- Because tRNAs do not alter the genome, there is no risk of off-target DNA edits, genotoxicity, or potential concerns associated with gene editing.


The next step in genomic medicine
Our therapies operate at the critical juncture where genetic information is translated into the proteins responsible for cell function.
Scroll downProtein editing for genetically driven diseases
Our elegant approach overwrites faulty genetic instructions and enables the cell to produce functional proteins from flawed blueprints.
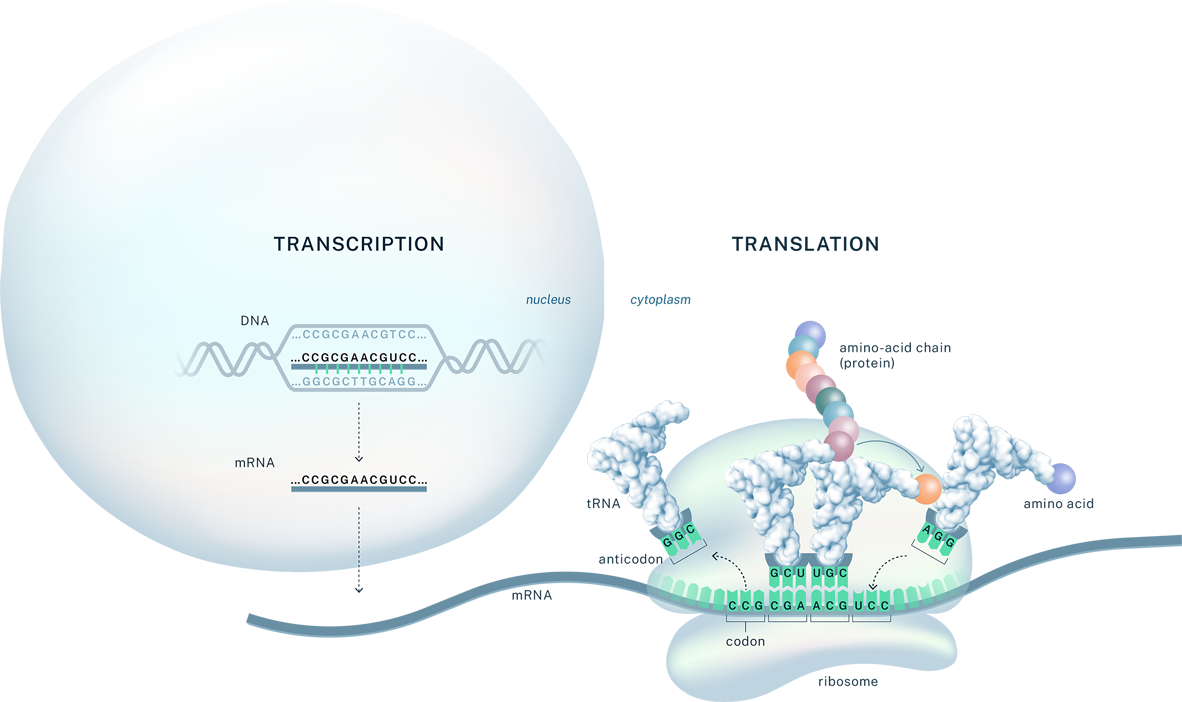
During translation, tRNAs and ribosomes assemble a protein by joining together amino acids according to instructions contained in the mRNA transcript. tRNAs, acting as molecular interpreters, add the genetically specified amino acid by matching each three-base pair mRNA codon to its complementary tRNA anticodon.
Our anticodon engineered (ACE) tRNAs are designed to treat disease by ignoring the faulty instructions of mutated mRNA codons, delivering instead the cognate amino acid needed to produce a functional protein.
Redefining genomic medicine
Protein editing is a simple, elegant approach to overwriting common genetic errors. It offers distinct advantages over other treatment options for genetically defined diseases.
A nonintegrating genetic medicine
Seamless fit within the cell
- Anticodon engineered (ACE) tRNAs are expressed, modified, charged, and metabolized like endogenous tRNAs. Aside from overwriting premature termination codons, they do not impact the cellular translation machinery.
- ACE tRNAs do not change the natural regulation of the target gene expression so the resulting protein is produced at physiological, endogenous levels.
Targetable to specific cells
- Because of their small size (<100 nucleotides), ACE tRNAs can be delivered via multiple delivery options that can be optimized for a target cell type or tissue.
- Maximizing expression in target cells allows the resulting protein to undergo normal post-translational modification and regulation while minimizing ectopic expression.
Broad applicability across thousands of genetic diseases
- tRNA-based therapies are gene agnostic — they target specific types of mutations shared across thousands of genetic diseases and cancer. This versatility allows one ACE tRNA to treat a broad spectrum of indications.
